Levels of the Memory Hierarchy
제어의 주체는 OS
The Principle of Locality
Program은 특정 시점에서 보게되면 address space 중 일부분에서 움직임
Temporal Locality - 참조된 byte는 또 참조될 가능성이 높다(loops, reuse)
Spatial Locality - 참조된 byte의 인접한 곳이 참조될 가능성이 높음(프로그램이 순차적임, array access)
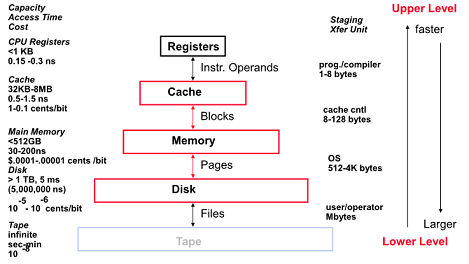
Memory Hierarchy: Terminology
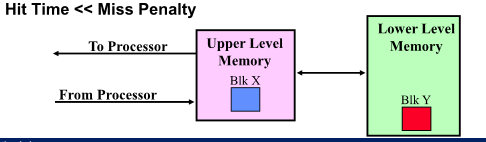
Process 는 memory address를 genearge 하는데 upper level 에 존재하면 Hit 아니면 Miss
Cache Measures
Hit rate 값이 매우 커 차이가 많이 안나므로 Miss rate를 Cache 측정하는데 사용
1, 3, 5% 에 따라 3배 5배 차이남
Average Memory-access time = Hit time + Miss rate * Miss penalty(ns or clocks)
Miss Penalty = access time + transfer time
(lower level로 부터 block을 교체하는데 까지 걸린 시간)
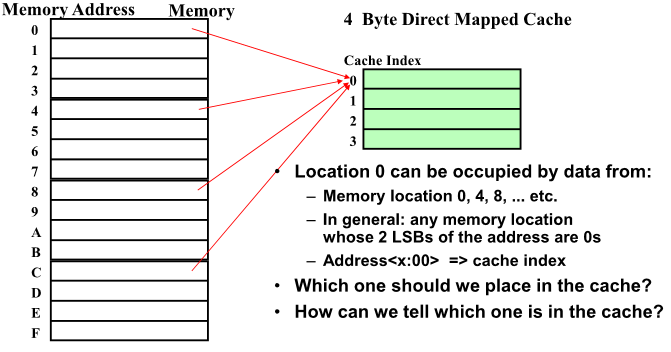
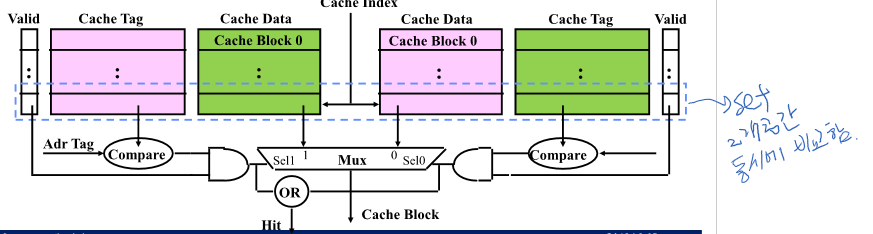
Simplest Cache: Direct Mapped
Memory와 Cache 간의 Managing 하는 기본 Unit = Blocks
Block를 1byte라 가정
Cache 가 4byte Direct Mapped Cache 일 때 매핑
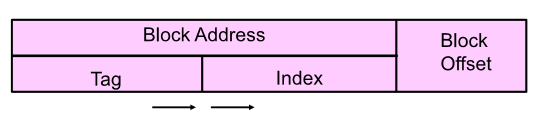
Memory를 캐쉬의 크기로 나누어 상대적 위치로 1:1 매핑 되어짐 -> Direct Mapped
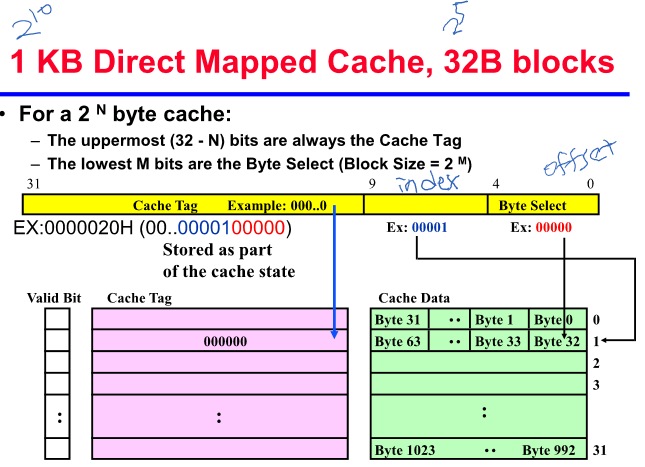
1KB Direct Mapped Cache, 32B Blocks
Two-way Set Associative Cache
독립적인 모듈 2개를 연결시킨 구조
4 Questions for Memory Hierarchy
1. 블락을 캐쉬 어디에 위치시킬까(Modulo)
2. 캐쉬가 upper level에 있을 때 어떻게 발견?(Tag 필드로 비교해서 암)
3. 미스가 발생하면 누구를 내보낼지(LRU, Random)
4. Write할 때는 기달렸다 Write Back 하거나 등
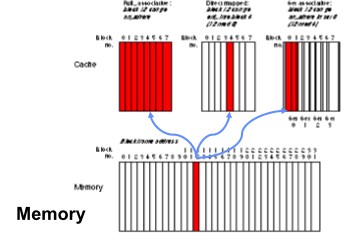
Q1 : Where can a block be placed in the upper level?
LKN
L = Block Size
K = Associative(N way의 N 의미)
N = Set의 개수
N이 1인경우 Fully Associative
K = 1 인경우 direct mapped
12MOD 8 = 4
12 MOD 4 =0(set가 2개이므로) -> 2slot중에 들어가면됨
Q2: How is a block found if it is in the upper level?
tag를 통해 비교
Q3: Which block should be replaced on a miss?
LRU(Least Recently Used) - 안쓰고 있는 block을 내보냄
FIFO(LRU is beeter than FIFO) - 들어온 순서대로 block을 내보냄
Random - 아무 block 이나 내보냄(실험 해본 결과 random이나 LRU 해도 8-way인 경우 성능 비슷)
Q4: What happens on a write?
loads가 26%, stores 10% 임
read가 common case고 read를 잘할 수 있도록 캐쉬를 만들어 주어야함
write할 때 read에 영향을 주지 않도록 설계해야함
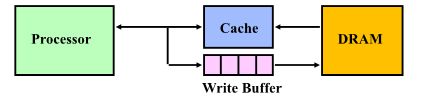
Write through - cache에 한 개의 데이터 쓰고 write buffer를 운용
FIFO로 write 함
Write back - 데이터는 Cache에만 write 되고 수정된 block이 memory로 replace 될 때 한번 씀
Modify된 block인 경우(dirty) replace 될 때 memory에 write
WT는 read miss가 writes를 야기시키지 않음
WB는 같은 location에 반복해서 wirte 하지 않음
Write Strategy for Allocation
write miss 시 캐쉬 할당 여부(Write allocate)
Write allocate는 read write 구분 없이 miss 시 캐쉬에 넣는것이고 No write alocation은 read만 캐쉬에 넣음
No write alocation이 효과가 더 좋음
A Modern Memory Hierarchy
지역성을 활용해 무지 많은 메모리가 싼 값으로 제공하는 척하는 것이 메모리 계층구조의 핵심 개념
Present the user with as much memory as is available in the cheapest technology
Provide access at the speed offered by the fastest technology
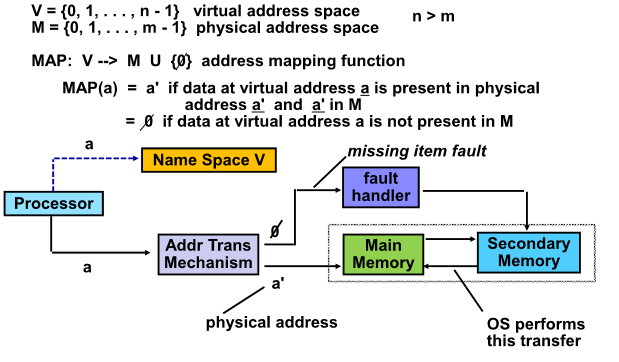
Basic Issues in VM System Design
메인메모리와 디스크간에 단위는 Page
메인메모리에 page가 없을 때 page fault 라 하고 이를 디스크에서 가져옴
CPU는 프로세스가 할당될 때 마다 VM을 할당
매번 Virtual Address를 generate하면 이를 Physical Address 로 바꾸어 Cache 등이 작동하도록해주어야함
Addressing Map
Virtual address space
Physical address space 가 주어질 때
V -> P로 전환하는 함수를 설계해야함
CPU는 Virtual address로 구동
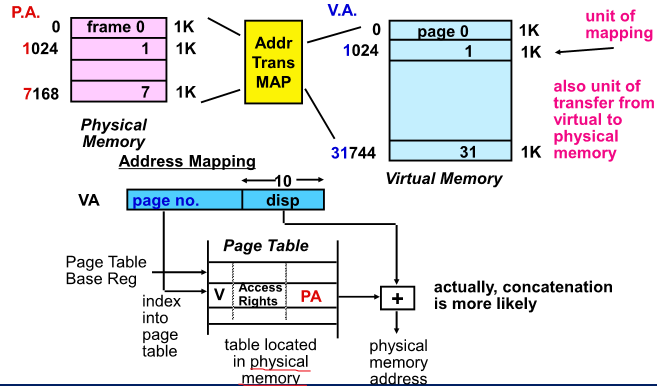
Paging Organization
Page Table을 통해 Physical address 를 뽑아냄
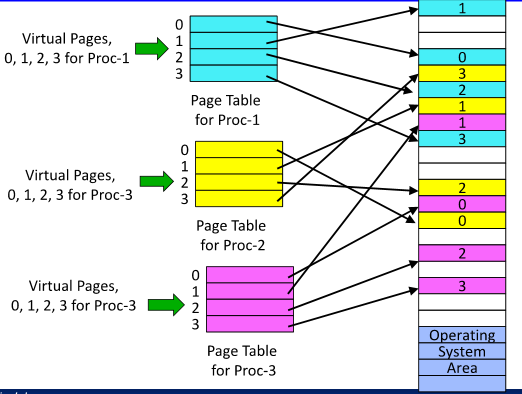
Virtual Address/Page Allocation
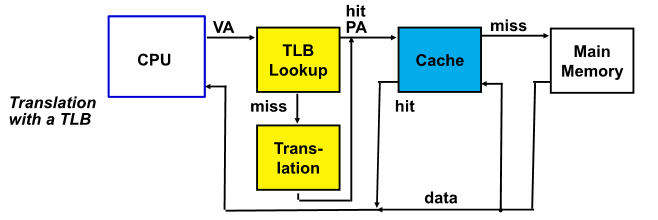
Translation Look-Aside Buffers
VA를 PA로 변경하기 위해 Pagetable이 메인 메모리에 있어야함
Access를 빨리하기 위해 캐쉬를 썼는데 VA를 써서 메모리 Access를 계속해 변경해 사용해야함
여기서 가장 많은 시간이 걸려(critical section) 문제가 생김
Address Translation 스피드를 개선하기 위해 사용하는 것이 TLB
TLB - Page table의 현재 참조가 되고 있는 일부 entry만을 보유해 유지하는 특별한 캐쉬(Address Translation 용)
128 ~ 256 정도 작은 cache임
Reduction Translation Time
Cache access 랑 TLB access를 동시에 하게 하는 것이 overlapped Cache & TLB Access
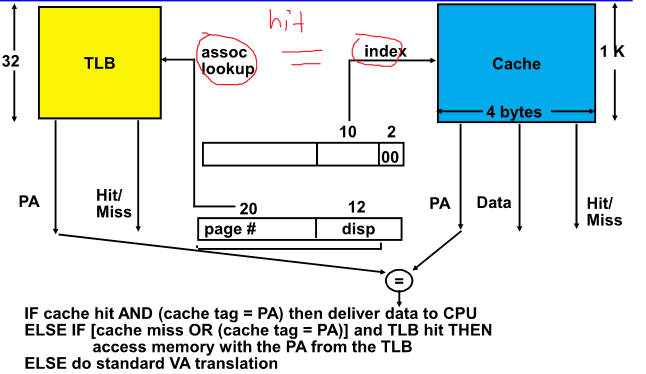
Problems With Overlapped TLB Access
associate를 증가시키면 캐쉬를 좀 더 크게 사용 가능
or
Page size를 8K로 증가 시켜야함
Recent Virtual Memory
예전에 작은 메모리 공간을 디스크 처럼 크게 사용하도록 설계되었음
Protection으로 최근에도 사용하는 목적으로 바뀜
(Today VM allows many processes to share single memory without having to swap all processes to disk)
Summary
Cache Design Space
1. Target average access time 결정
2. Cache와 메모리 특정 DRAM과 Cache를 결정하면 miss rate 결정됨
3. Miss rate를 커버할 수 있는 L K N을 결정하면 캐쉬메모리 설계 끝남
TLB, Virtual Memory
Memory Hierachy
최근 protection이 더 우선시 되는 상황이다