Static Hashing
- Hash function h 는 search key값으로 쓸 수 있는 모든 값을 bucket의 주소로 바꾸어 주는 함수
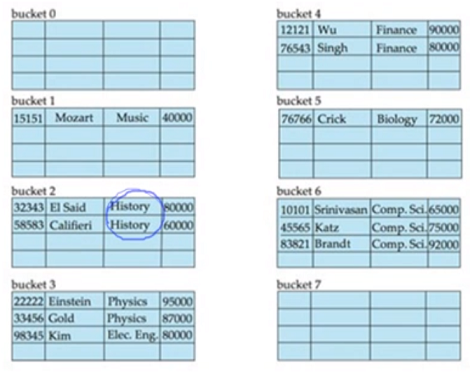
deptName에 따라 Hash되어 구성되어 있는 예제
Hash Functions
- ideal hash function 은 uniform 해야함(모든 값에 대해)
- random: search key value가 어떤 분포를 가지던 간에 버킷에 assign 되는 records가 동일하다면 random
이론적으로 이상적이지 실제로는 거의 불가
Handling of Bucket overflows
- bucket 이 너무 적을 때
- Skew in distribution of records
Overflow를 줄일 수는 있지만 완전히 없앨 수 는 없음
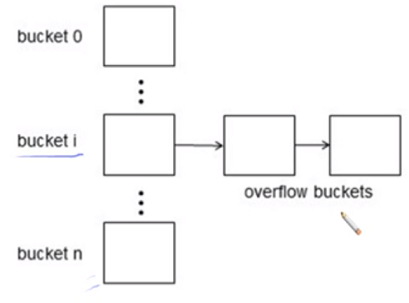
Overflow chaining
linked list로 이어주는 방식
Open hashing
버킷 i에 공간이 다차면 다음 record는 순차적으로 다음 bucket 에 들어감
record 를 검색함에 있어 hash 값이 bucket i 만 검색하지 않고, 밑에있는 page 도 다 같이 검색해야하는 문제점이 발생함
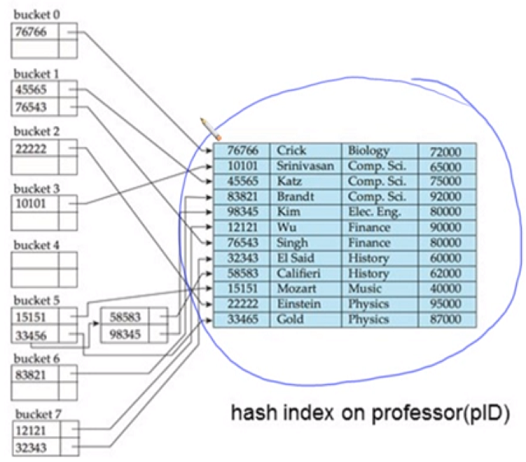
Hash Indices
data file 보다는 index를 구성하는데 많이 쓰임
hash index는 항상 secondary indices 여야함(실제 record 순서와 무관)
bucket 5에 overflow chaining 단 것 보임
Static hash는 hash function 값이 한번 정하면 변경되지 않음
record가 계속 증가되게 되면(data file) 계속 bucket 의 record가 증가되어 거의다 overflow chain으로 연결되어 있음
hash는 데이터를 빨리 찾아야하는데… 검색시간이 길어짐
Deficiencies of Static Hashing
데이터베이스는 시간에 따라 grow하고 shink 할 수 있음
데이터가 커지면 static hashing 은 대응이 힘듬, over bucket 도 증가
-> buckets 의 개수를 유연하게 변경할 수 있는 것이 좋은 solution임
Dynamic Hashing
database가 grow, shink 할 때 좋음
hash function이 dynamically 변경될 수 있음
Extendable hashing - dynamic hashing 중 하나의 형태
Extendable hashing
- hash function이 32bit integers를 생성함
- 앞의 몇자만 사용할지의 prefix 길이를 ibits라 함 0<= i <= 32
- 처음은 i=0(2^0 = 1) 이고 grows, shinks 할 때 i 값이 변함
- 실제 buckets의 개수는 2^i 보다 작음
- bucking 에 대해 coalescing 과 splitting 가능함
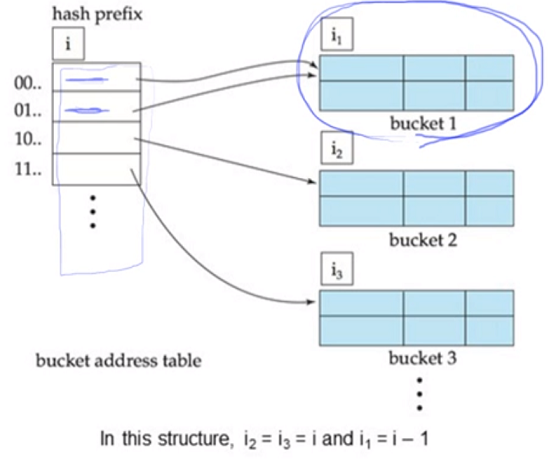
Extendable Hash Structure
00, 01은 아직 bucket 개수가 적어 하나의 bucket 안에 있음
- Eash bucket j stores a value i(j)
- search key K를 어떻게 찾는지?
- h(K) 해서 X 가 나오면
- X의 i bit 만 가지고 원하는 bucket 을 찾아가면됨
- insert 는 bucket을 찾아가 공간이 있으면 삽입하고 아니면 bucket을 split 함
split의 2가지 경우
- i>i(j) - more than one pointer to bucket
- 그냥 insert 하면됨
- i=i(j) - only one pointer to bucket
- i를 하나 증가시켜 bucket address table이 dobule size 됨
- 기존 entry 재 분배 후 insert
delete
- 기존 record가 다 delete 되면 bucket remove
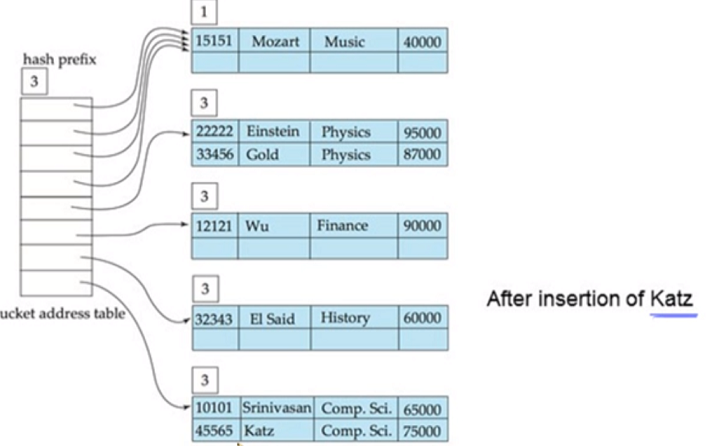
Extendable Hash Example
dept_name 가지고 hash 주소 할당 예제
처음 h부터 i bit 만큼을 보고 hash bucket을 찾아감
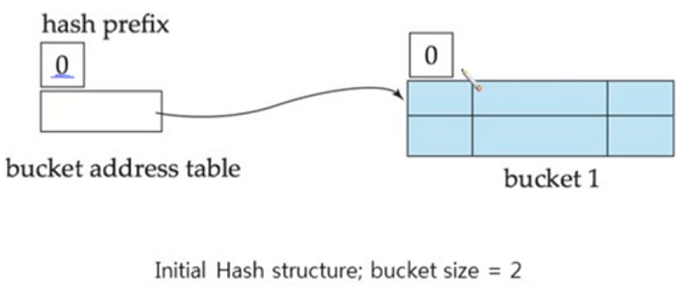
initial hash 구조
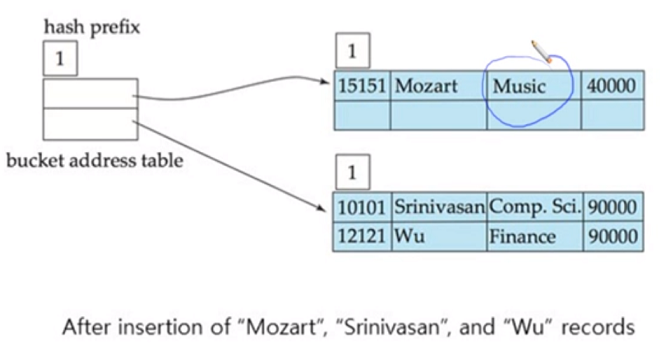
insertion 하면 music은 hash 값이 0, Comp.Sci와 Finance는 hash 값이 1
bucket address table은 1bit를 가지고 hash 시킴
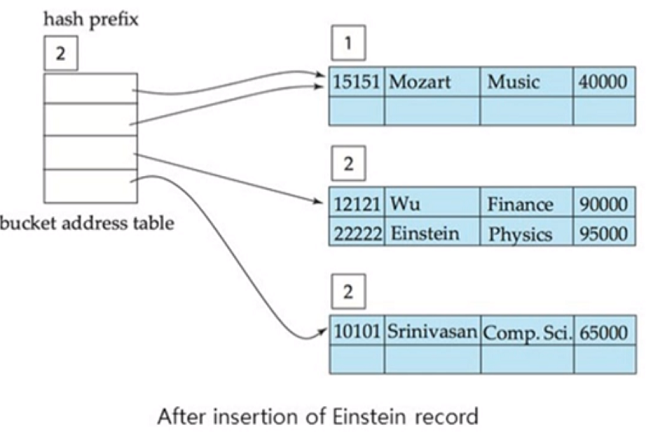
Einstein을 넣으면 Physics dept_name이 추가적으로 들어오는데 hash prefix 하나 더 증가됨
단 Mozart 쪽 보면 1로 여전히 하나의 prefix 만 봄
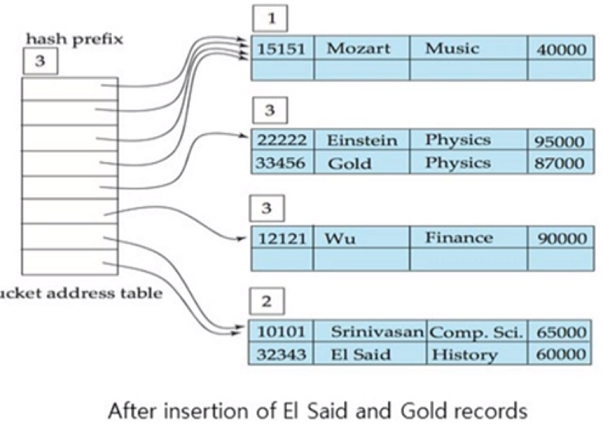
EI Said 은 history 고 해당 h값이 11로 들어갈 수 있어 그냥 삽입
Gold를 삽입하면 원래 Wu가 있는데 들어가야되는데 꽉차서 bucket 이 split 되고, bucket address table 1증가되 size 가 두배로 증가됨
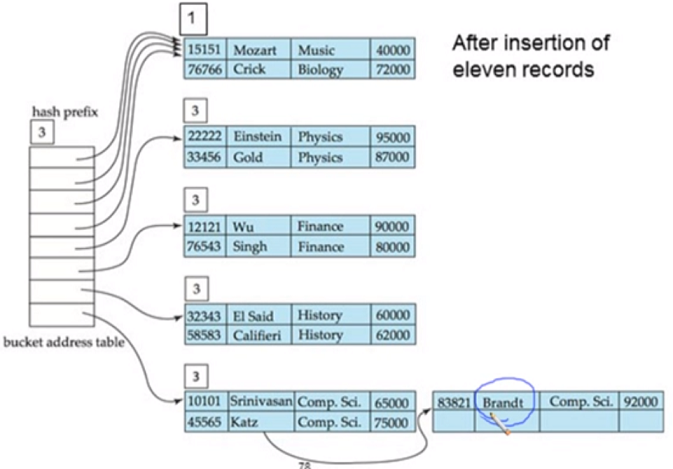
Katz들어오면 아래 bucket 도 split 되지만 bucket address table은 하나 증가시킬 필요 없음
split을 안하고 overflow를 chain으로 연결시킴
-> split을 해도 같은 해쉬 값을 가지므로 해결되지 않기 때문에 linked 로 연결 시킴
Extendable Hashing vs Other Schemes
Benefits of extnedable hashing
- 파일이 증가해도 성능 유지
- 데이터 파일에 따라 space 차지 변화됨(Minimal space overhead)
Disadvantages of extendable hashing
- record를 찾기위해 extra level of indirection이 발생 -> bucket address table이 추가되었으니까~
- bucket address table이 매우 커질 수 있음
- bucket address table의 사이즈를 변화시키는 것이 비싼 연산임
Comparison of Ordered Indexing and Hasing
- Hashing은 특정한 값을 가지는 record 를 찾을 때 좋음
- range queries의 경우 ordered indices 가 더 좋음(B+-Tree)
Multiple-Key Access
Use multiple indices for certain types of queries
select pID from professor where deptName=’CS’ and salary=80000;
두개의 index에 각각 pointer를 찾아 intersection 하여 찾음
Indices on Multiple Attributes
두개의 값을 보아서 하나의 index를 만들 수 있음
(deptName, salary)
Lexicographic ordering: (a1, a2) < (b1, b2)
- a1 < b1 or
- a1=b1 and a2<b2
deptName에 대해 잘되지만 salary에 대해 같을 때는 index가 쓸모 없어짐
-> a1 < a2 and a2 = b2(dept_name <’finance’ and salary = 80000)
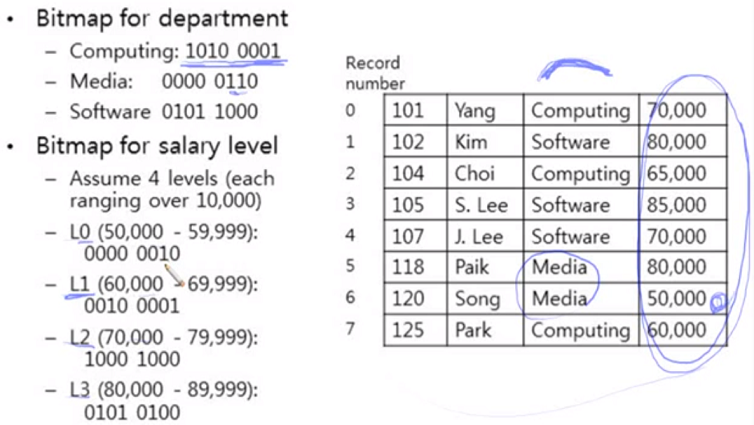
Bitmap Index
Bitmap은 여러 attribute 조건을 동시에 검색하는데 최적화 되어 있음
attributes의 값의 개수가 상대적으로 적어야함(ex, gender - 남, 여, range를 나누어 사용하는 것도 가능함)
bitmap은 bits의 array가 되고 bit 연산을 가지고 검색하고자하는 record를 빨리 찾는 방식
record의 개수만큼 bitmap이 생성되고 해당 record의 값이 맞냐 아니냐에 따라 0, 1로 되어 있음
위의 bitmap을 이용해 Computing과 L2 인 Salary level 인 사람을 검색하면 두 bitmap을 intersection 시켜서 처리하면 해당 record 나옴
100110 and 110011 = 100010 bit 연산(AND, OR, NOT)이 빠르므로 빠르게 matching 되는 tuple을 찾을 수 있음