Basic Concepts
- 색인은 데이터에 접근할 때 speed up을 위한 목적임
- 책안에 index와 같은 것이 DB에 적용된 것이라 보면됨
- index file은 <search-key, pointer> 형태의 records로 구성됨
- index record가 모여있는 것이 index file
- 2가지 종류의 indices
- Ordered indices: Search key가 정렬된 상태
- Hash indices: Search key가 hash function으로 분류되어 있는 것
Ordered Indices의 대표적인 것이 b+ tree
Ordered Index
index entries가 정렬되어 저장되어 있는 것
- Primary index(clustering index)
- 색인에 따른 정렬에 따라 data file도 정렬되어 있는 것
- data file은 한개 존재 하기 때문에 data file 당 하나만 존재할 수 있음
- Secondary index(non-clustering index)
- data file은 정렬되어 있지 않지만 색인만 정렬된 상태
- data file과 상관 없기 때문에 여러개 존재 가능함
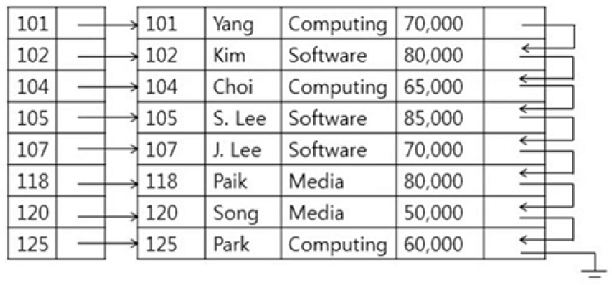
Primary index: Dense Index
- Dense index
professor relation이 있다고 가정하면 위의 모든 record에 대한 index가 point를 가지고 있으면 dense index라 함
Index record appears for every search-key value in the file
DeptName으로 index 되어 있고, DeptName의 모든 index에 대해 색인이 되어 있으니 Dense index 임
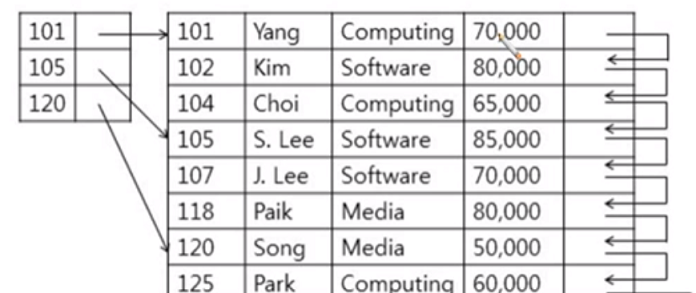
Primary index: Sparse Index
search-key 중 일부분에 대해 index records 가 생성되어 있는 것
Sparse index가 되려면 data file이 정렬되어 있어야함
정렬되어 있지않으면 sparse index는 데이터를 효율적으로 찾을 수 없음
Compared to dense indices
- Less space
- less maintenace overhead for insertions and deletions
- 다만, data 를 찾는데 시간이 더 걸림
좋은 sparse index 란?
- data는 search key에 대해 sort 되어야 함
- block의 가장 적은 값을 가져야함(data block이 block 당 정렬되어 있으면 block당 index entry 를 만드는 것이 좋음)
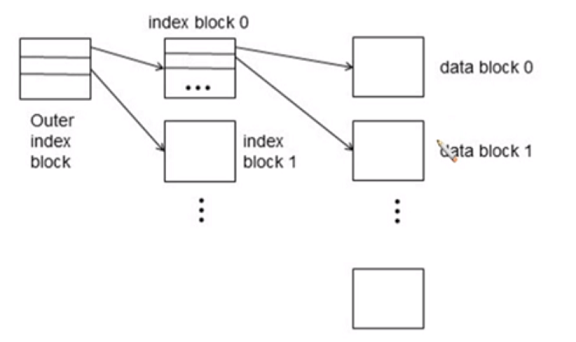
Multilevel Index
index 자체가 multilevel로 구성이 가능
- data file에 대해 index 를 만들었는데 index 가 너무 커서 index 자체의 index를 더 만드는 것
- disk 에 있는 primary index를 sequential 로 처리해서 primary index 위에 sparse index를 하나더 만듬
- primary index file은 Inner index
- primary index file에 대해 sparse index를 만든 것이 Outer index
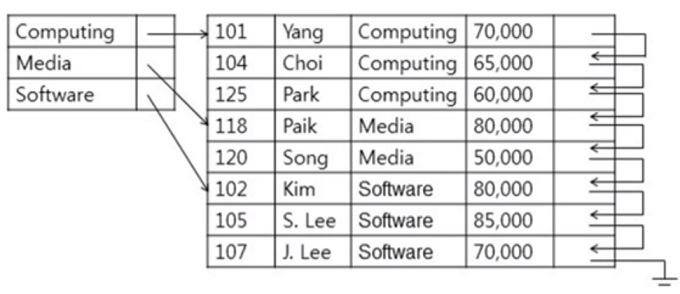
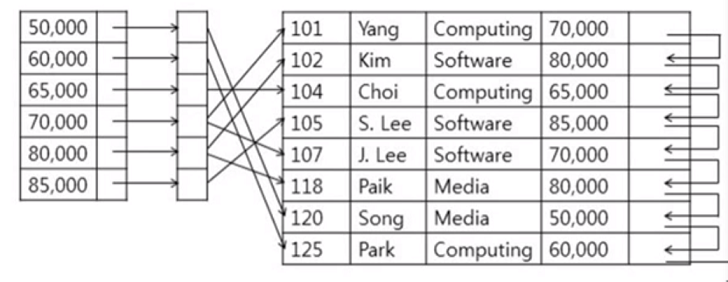
Secondary Index
professor relation이 pID에 대해 sequentially 하게 정렬되어 있지만 특정 월급으로 search 하기를 원한다고 가정
data file이 월급으로 정렬되어있지 않음
이런 경우 반드시 secondary index 만들 때 dense 해야함(Secondary indices have to be dense)
위에 보면 Secondary index는 dense 하고 그 앞의 outer index는 정렬되어 있는 것을 볼 수 있음
Primary vs Secondary Indices
Sequential scan은 primary index가 더 효율적이고, secondary index는 비용이 비쌈
B+-Tree Index
데이터베이스 응용에서 제일 많이 사용하는 index
indexed-sequential file의 대안!
- index file이 커질 수록 performance 저하 -> 주기적으로 전체 index file을 재구성 해주어야 하기 때문에
장점이 단점보다 훨씬 많음
장점: 자동으로 small and local changes 에 대해 reorganizes 함
단점 : insertion and deletion overhead, space overhead
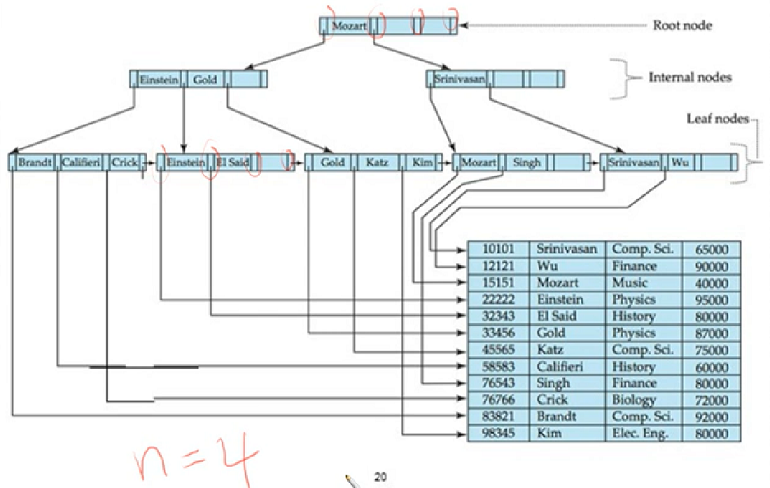
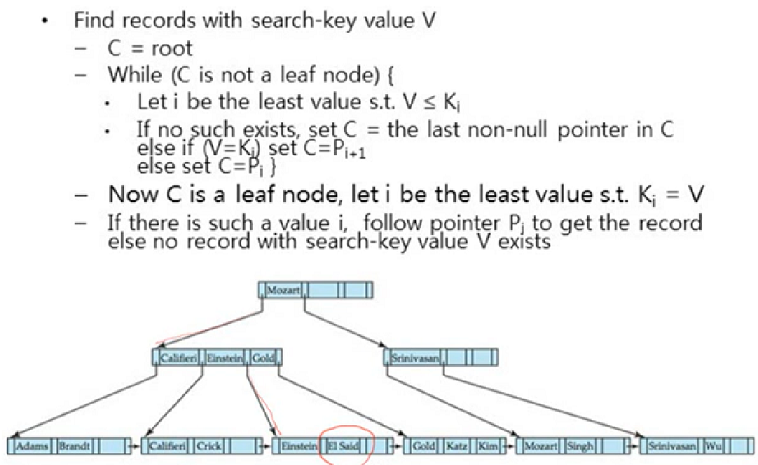
Example of B+-Tree index
n=4 인 경우
사람 이름으로 index를 만들었고, datafile은 사람 이름 순서가 아님
leaf node 에 있는 값은 정렬되어 있음
leaf node는 dense index 임(data file의 모든 search key가 다 나옴)
Root, Internal은 sparse index 임
n=4 여서 최대로 갖는 pointer 개수는 4가지임
B+-Tree at a glance
- B+-tree 는 root 에서 leaf 까지의 길이가 모두 같다(동일한 시간으로 data를 찾을 수 있는 장점)
- root 와 leaf가 아닌 노드는 ┌n/2┐ 와 n개 사이의 children (pointer)개수를 가짐
- leaf 노드는 ┌(n-1)/2┐ 와 n-1 사이 값을 가짐
- root가 leaf가 아니면 최소 2개 가져야함
B+-Tree Node Structure
[P(1), K(1), P(2), K(2), … , P(n-1), K(n-1), P(n)]
n은 pointer의 개수이고 n-1은 값의 개수
leaf node이면 records or buckets 에 대한 pointer 임
Search key들은 ordered 되어 있음
- K(1) < … < K(n-1)
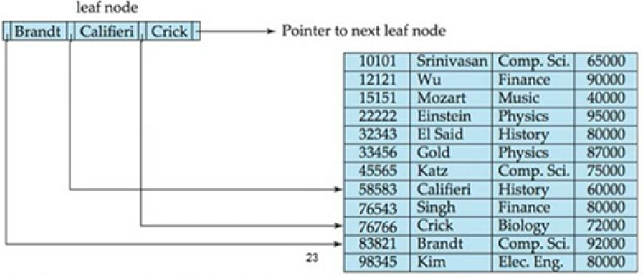
Leaf Nodes in B+-Tree
값의 왼쪽을 쫒아가면 값이 나옴
p(n) 은 다음 leaf node를 가지는 포인터임
RID = PID + slot #
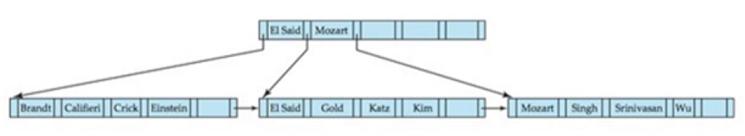
Non-Leaf Nodes in B+-Tree
muti-level sparse index form
[P(1), K(1), P(2), K(2), … , P(n-1), K(n-1), P(n)]
K(1) <= P(2) < K(2)
Example of B+-Tree(n=6)
- Leaf nodes must have between 3 and 5 values(┌(n-1)/2┐ and n-1, with n = 6)
- Non-leaf nodes other than root must have between 3 and 6 children(┌n/2┐ and n)
- Root must have at least 2 children
모짜르트의 경우 정의를 K(1) <= P(2) < K(2) 이와 같이 해서 오른쪽을 쫒아가야 값이 있음
B+-Tree height
B+-Tree를 쓰면 levels 가 상대적으로 짧음
- root 밑에 있는 level이 가지는 최소 값이 2*┌(n-1)/2┐ values
- Next level 은 2 * ┌n/2┐ * ┌(n-1)/2┐
- 또 Next level 은 2 * ┌n/2┐ * ┌n/2┐ *┌(n-1)/2┐
- K개의 search key values 가 있을 때 tree 의 height는
를 넘지않음
- 1000000(1million) search key의 값에 대해 n = 100 일 때 log50(1000000) = 4 로 4번 만에 access가 가능함
굉장히 데이터를 빨리 찾을 수 있는게 장점임
Queries on B+-Trees
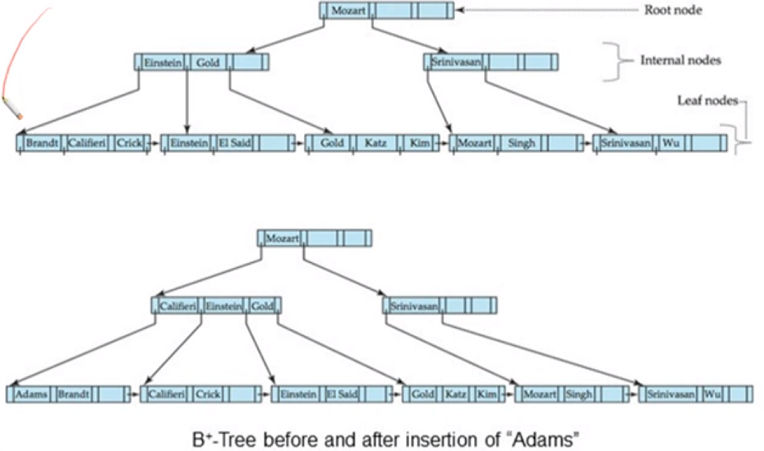
Insertion Example
Adams가 첫번째 leaf node에 들어가게 되어 두개로 쪼개지고, Califeri가 위로 올라가게됨
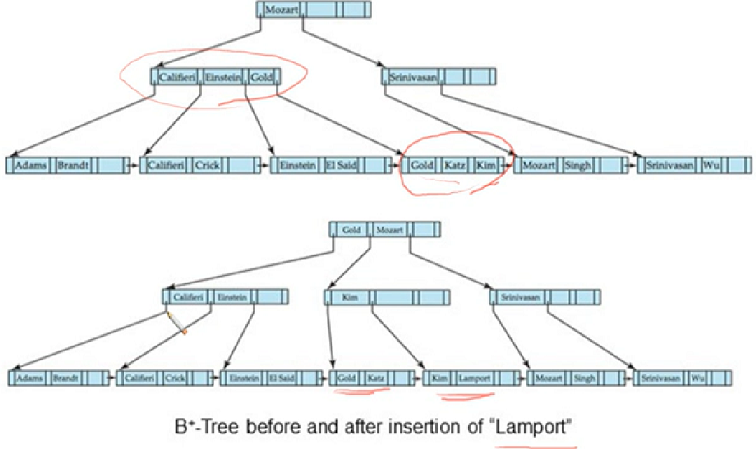
Lamport 를 넣고 Kim이 올라가는데 또 꽉차서 두개로 쪼개지고 새로운 record가 생성되어 거기에 kim 이 들어감
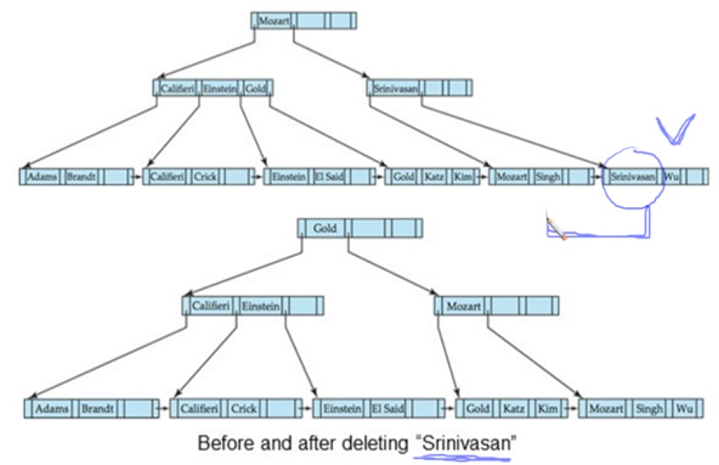
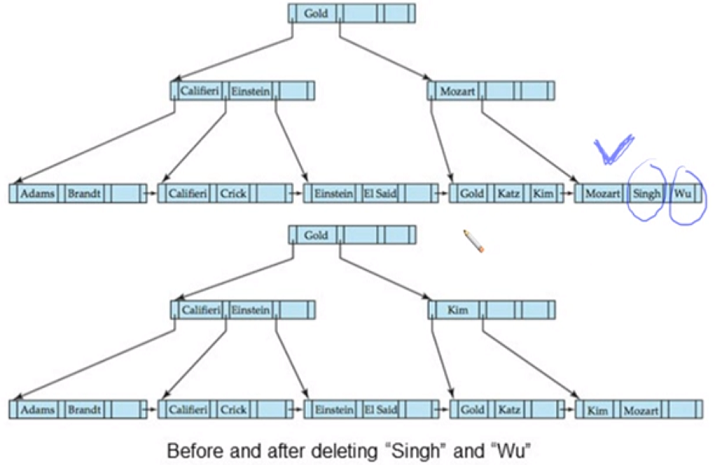
Deletion Example
undeflow 일때 merge하거나 redistribution 함
- merge 할 때 parent 로 부터 삭제된 pointer 없애는 recursive 한 작업 필요
- 옆에 sibling 노드가 많아 merge 할 수 없을 때 pointer 를 redistribution하여 절반 씩 나누면 됨
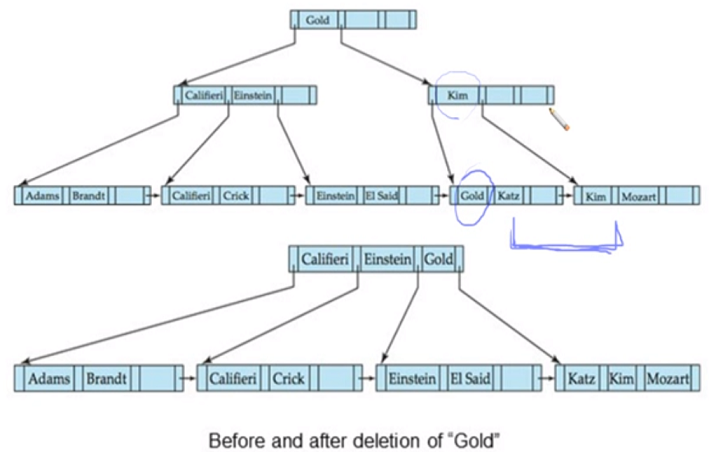
Srinivasan이 없어지면 두개 merge 시켜 하나의 node로 되고 위의 Srinivasan도 지우게되면 또 underflow가 나 pointer 를 redistribution 시켜 Gold 가 올라가고 Mozart가 아래로 내려옴
Singh 와 Wu 삭제하면 underflow 나고 옆에 꽉차 하나의 노드에 들어갈 수 없어 재분배 시킴 -> Kim이 올라가는 것으로 처리
root 까지 전파되는 deletion
leaf node에 gold가 없어도 non-leaf에만 gold 존재하는 것 주목
B-Tree Index
B-Tree는 nonleaf nodes에 있는 Search key 값은 안나타남
record 값에 대한 index를 구성하는 것임
leaf나 nonleaf 나 data 에 대한 pointer 를 가져 중복을 없앤 것임(leaf 에 있는 것이 반드시 non leaf 에 나오지 않아도 됨)
장점: leaf 노드데 도달 전에 search 키를 찾을 수 있음
단점: leaf 전에 찾는 것이 매우 적음, non-leaf node 가 너무 커짐, insertion and deletion이 B+-Tree에 비해 어렵고 구현도 어려움